Heel Lift for Achilles Tendinopathy: Understanding Benefits and Proper Use
Achilles tendinopathy can be a painful condition that affects many individuals, especially those who participate in sports or engage in regular physical activity. The discomfort often stems from overuse of the Achilles tendon, leading to inflammation and degeneration. Heel lifts provide a beneficial approach to managing this condition by reducing strain on the tendon and improving overall function.
Some are still looking for legitimate methods to help them reduce the pain and be active. Heel lifts sit inside your shoes, raising the heel. This raised angle relieves strain around the Achilles tendon by altering how weight is distributed. If you suffer from Achilles tendinopathy, studies suggest introducing heel lifts into your routine can make a big difference.
Heel lifts can also be part of an overall treatment plan that includes targeted exercises and stretches to strengthen the calf muscles. These techniques will not relax the pain and cooling of your body but also shield you from more injury. A broad-based approach also would go a long way in delivering durable therapycures to devise achilles tendinopathyaging friendly.
Understanding Achilles Tendinopathy
Achilles tendinopathy refers to a range of conditions affecting the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This section will explore the anatomy of the Achilles tendon, the symptoms and diagnosis of tendinopathy, and the different types of this condition.
Anatomy of the Achilles Tendon
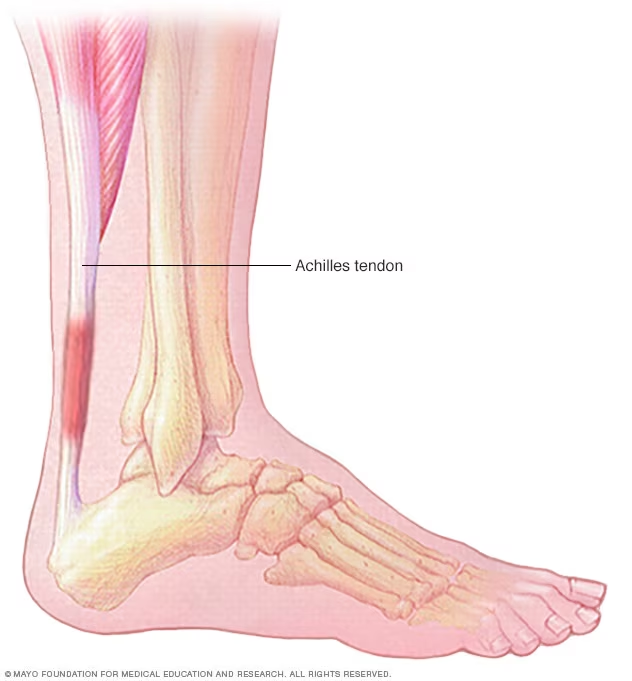
Your Achilles tendon is the largest in your body and runs along back of ankle. It links the calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to the heel bone, calcaneus. This important tendon is required for walking, running and jumping as it allows movement of the foot plus force production.
This experiences a good deal of stress with exercise, and the tendon takes it in stride. It can support with 12.5 times body weight in explosive exercises This arrangement however can be damaged by overuse, poor biomechanics or rapid changes in activity. One of the most important parts about this heel anatomy is identifying that it exists, which can help you see what factors may cause issues such as Achilles tendinitis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy can vary but often include pain along the tendon, especially during movement. Patients may experience stiffness in the morning or after periods of rest. Swelling or thickening of the tendon may also occur, along with tenderness to touch.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and a review of the patient’s symptoms and activity levels. Healthcare providers may perform specific tests to assess tendon function and pain responses. Imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI can be used to confirm the diagnosis by examining tendon structure and determining the severity of the injury.
Types of Achilles Tendinopathy
There are two main types of Achilles tendinopathy: mid-portion and insertional.
Mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy occurs in the central part of the tendon, usually about 2-6 cm above the heel. It is often seen in runners and is linked to overuse or improper training techniques.
Insertional Achilles tendinopathy, on the other hand, affects the area where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. This type is commonly associated with conditions like bursitis and can occur in individuals who wear shoes with inadequate heel support.
Chronic cases of either type may lead to tendon degeneration and increased risk of further injury, making early intervention important.
Role of Heel Lifts in Treatment
Heel lifts play an important role in managing Achilles tendinopathy by reducing pain and improving function. They can provide relief by altering foot mechanics and reducing strain on the Achilles tendon. Understanding their benefits and how to select the right type is crucial for effective treatment.
Benefits of Using Heel Lifts
Heel lifts can help ease Achilles tendon pain by elevating the heel, which decreases tension on the tendon. By raising the heel a few centimeters, these lifts change the mechanics of walking and running. This can alleviate discomfort and improve mobility.
Research indicates that using heel lifts can be beneficial compared to other treatments. For example, studies show that heel lifts can reduce pain severity significantly, often outperforming eccentric exercise programs in short-term results.
Additionally, in-shoe heel lifts are easy to use. They can be inserted into regular shoes, making them a convenient option for daily activities. This accessibility helps users maintain an active lifestyle while managing their condition.
Selecting the Right Heel Lift
Selecting the right heel lift is important for proper treatment. Heel lifts are a type of insert that typically come in heights varying from 6mm to 12mm. The selection of the height should be based on every individual tolerance and comfort.
It is likely best to consult with a healthcare provider about what may be most ideal for your particular case. Others might need customly-made lifts in order to have better alignment.
Find heel lifts constructed of sturdy materials like foam, and make sure they are supportive enough so as not to lead to excessive ankle pain.
Proper fitting is vital. If improperly sized, the foam heel lift can create more problems such as changing your gait or generating further discomfort. It needs to be checked on a regular basis in order to continue offering the type of support it has been chosen for.
Integrating Heel Lifts with Exercise Therapy
Combining heel lifts with exercise therapy can enhance treatment outcomes for mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy. This approach allows for gradual adjustments in load and can improve patient compliance with therapeutic exercises.
Exercise Protocols
When treating mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy, exercise protocols often focus on calf muscle eccentric exercises. These exercises aim to strengthen the calf muscles and improve tendon function. Common exercises include:
- Single-leg heel drops: Standing on a step and lowering the heel down slowly.
- Calf raises: Lifting the body up on the toes and then lowering it back down.
Incorporating heel lifts can modify the baseline mechanics of these exercises, reducing strain on the Achilles tendon.
This adjustment may allow patients to perform exercises more comfortably while promoting healing. Consistent practice, typically three times per week, is important for best results.
Combining Heel Lifts with Eccentric Exercises
Heel lifts embedded into eccentric exercise programs may offer the largest benefit for patients with Achilles tendinopathy. A comfortable pair of heel inserts can lift your heel, thereby decreasing the amount of stress placed on this tendon while you exercise.
For example, when doing calf raises, using a heel lift can help reduce pain. This can allow a slower progression in intensity which wont overload the tendon. This could help patients complete more repetitions.
The key is to carefully monitor progress and make pain-led changes in wearing heel lifts. A physical therapist is able to do this well since they know how to modify the exercises for each individual patient.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Heel Lifts
Assessing how effective heel lifts are for treating Achilles tendinopathy involves examining clinical studies and gathering data on patient experiences. This section discusses research findings and measures that reveal how heel lifts may impact pain and functionality in patients.
Clinical Studies and Research Data
Several clinical studies have explored the effectiveness of heel lifts for mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy. Most research indicates that heel lifts can significantly reduce pain levels. For instance, a study involving 92 participants compared heel lifts to calf muscle eccentric exercises.
The results showed notable reductions in pain for those who used heel lifts, with data collected using pain scales. Sample sizes in various trials ranged from small to moderate. Many studies emphasize the need for more rigorous research to evaluate the long-term benefits and any potential harms associated with heel lifts.
Patient Reported Outcomes
Patient-reported outcomes provide insights into how heel lifts influence daily life activities for individuals with Achilles tendinopathy. Many patients report decreased levels of pain and improved mobility after using heel lifts.
Surveys and questionnaires often measure pain intensity on a scale, allowing patients to express their experiences. Recent research indicates that many patients experience less discomfort and greater satisfaction when using heel lifts compared to traditional methods, such as eccentric exercises or no treatment at all.
Overall, patient feedback plays a critical role in understanding how heel lifts may improve quality of life, highlighting their importance in treatment plans.
Optimizing Footwear for Achilles Support
Selecting the right footwear is crucial in managing Achilles tendinopathy. Appropriate shoes and inserts can significantly improve comfort and support, helping to reduce strain on the Achilles tendon.
Choosing the Right Shoes
When choosing shoes, it is important to consider features that provide optimal support for the ankle joint. Shoes should have good cushioning to absorb shock during activities like running. A slight heel lift can relieve pressure on the tendon, allowing for a better foot position.
Look for shoes with:
- Arch support: Helps to maintain proper alignment.
- Cushioned heel: Reduces impact on the tendon.
- Wide toe box: Allows for natural toe splay.
Brands like ASICS and Brooks offer models that cater to these needs. Ensuring a proper fit is critical; shoes should not be too tight or too loose. The right footwear can make a noticeable difference in managing symptoms.
Custom Orthotics and Inserts
Custom orthotics and inserts can further enhance support for individuals with Achilles tendinopathy. They provide tailored support that aligns with the foot’s unique shape, which can alleviate excess strain on the tendon.
Key benefits include:
- Customized heel lift: Adjusts the height to optimize foot position.
- Additional cushioning: Offers extra comfort and shock absorption.
- Stability: Helps maintain proper gait mechanics.
Individuals should consult with a healthcare provider or a podiatrist to determine the most suitable options. Using the right orthotics can improve overall foot function and minimize discomfort during activities.
Considerations for Daily Activities
When managing Achilles tendinopathy, it’s important to consider how daily activities can affect the condition. The use of heel lifts may significantly influence gait mechanics and require some lifestyle adjustments.
Impact on Gait and Biomechanics
Heel lifts can alter the way a person walks. They may improve dorsiflexion, which is the upward movement of the foot at the ankle. This change can help reduce strain on the Achilles tendon during activities like walking and running.
As a result, walking speed may increase. This can lead to better physical activity levels, enhancing overall mobility. However, using heel lifts might also create a reliance on this support.
It’s crucial for individuals to monitor how changes in their gait affect their knees and hips. This insight helps avoid compensatory movements that could lead to further injuries.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating heel lifts may require adjustments in daily activities. Individuals should consider their choice of footwear. Shoes that accommodate heel lifts can provide additional comfort and support.
Physical activity should be balanced with rest to prevent overexertion. People can benefit from low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, to maintain fitness without stressing the Achilles tendon.
Stretching and strengthening exercises should be included in routines. This helps in gradually adapting to the changes brought by heel lifts. Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider can ensure that the condition is monitored effectively.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
Monitoring treatment progress for Achilles tendinopathy is crucial for assessing effectiveness and making necessary adjustments. Proper evaluation helps track improvement over time, aiming to reduce pain and increase function.
Assessment and Follow-up
Regular assessment is key to monitoring the effectiveness of heel lifts in treating Achilles tendinopathy. Clinicians often use valid measures, such as the VISA-A score, to evaluate pain and functional limitations. This score ranges from 0 to 100, where higher numbers indicate better function and less pain.
Follow-up appointments are essential to control the treatment’s progress over time. Most patients are evaluated at 4- to 6-week intervals during the initial phase of treatment. Active participation in these follow-ups helps identify the patient’s response to therapy.
During these visits, clinicians assess the duration and intensity of symptoms. They can then determine whether the heel lift provides adequate support or if further modifications are necessary.
Adjusting Treatment Over Time
As patients progress, adjustments to the treatment plan may be required. Factors such as pain levels and functional ability should be continuously monitored. If improvement plateaus, clinicians might consider increasing the heel lift height or integrating additional exercise programs.
It is also important to evaluate the bilateral condition of the patient’s feet. This includes ensuring that any treatments applied do not contribute to imbalance or other issues. Regular feedback about discomfort and effectiveness from the patient can guide these modifications.
The aim is to achieve consistent improvement in scores and functionality. Adjustments should be made to ensure sustained progress, allowing patients to gradually return to their normal activities.
Safety and Risk Management
Ensuring safety and managing risks associated with heel lifts for Achilles tendinopathy is crucial. Understanding potential risks and having a system for reporting adverse events can help maintain health-related quality and ensure effective treatment.
Identifying Potential Risks
When using heel lifts, there are specific risks to consider. One potential concern is the alteration it may cause in calf muscle function. Adjusting heel height can lead to overuse or strain on specific muscles, potentially resulting in discomfort or further injury.
Other risks include improper fitting or usage of the heel lifts. If they are too high or not adequately adjusted, patients may experience balance issues. This could lead to falls or additional musculoskeletal problems.
It is also essential to monitor for signs of skin irritation or pressure sores from prolonged use. Regular check-ups can help identify these issues early, preventing more severe complications.
Reporting and Managing Adverse Events
Reporting adverse events promptly is vital to ensure the safety of patients. If a patient experiences increased pain, discomfort, or any unusual symptoms after starting heel lifts, this should be documented and communicated to healthcare providers.
Management of these events involves a thorough assessment. Health professionals should evaluate the patient’s response to heel lifts and consider adjusting the treatment plan if necessary. This may include altering the heel lift height, switching to different orthotic devices, or integrating exercises to support calf muscle function.
Patients should be educated on the importance of reporting changes in their condition. Quick response to adverse events can prevent deterioration in health-related quality and improve overall treatment outcomes.