Foot Health: Essential Tips for Strong and Pain-Free Feet
Keeping your feet in top shape is vital for overall health, yet it often gets overlooked. Feet support the weight of the entire body and are essential for mobility. Taking care of them can prevent discomfort and future problems, such as bunions or athlete’s foot, and can even promote a more active lifestyle.
Maintaining proper foot hygiene and wearing the right footwear can make a significant difference in foot health. This includes regular washing, drying, and moisturizing, as well as wearing shoes that fit well and provide support. Activities like gentle exercises and stretches can also contribute to healthy feet.
If you experience persistent foot pain or conditions such as corns or heel pain, consulting with a specialist like a podiatrist can be beneficial. Experts in this field can offer targeted advice and treatment options, as mentioned by Foot Health Facts. Taking proactive steps will help keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
The Importance of Foot Health
Foot health is crucial as feet support the entire body. Each foot contains 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. When these components function together, they enable walking, running, and jumping comfortably.

Regular exercise for feet is essential. Simple exercises can enhance flexibility and strengthen muscles. This helps improve balance and reduces injury risks like ankle sprains. More information on exercises can be found at Harvard Health’s healthy feet exercises.
Ignoring foot health can lead to problems that affect the whole body. For instance, painful feet might impact mobility, leading to weight gain or reduced cardiovascular health. A strong base is critical to avoiding this cycle as noted in A strong base on foot health.
Common foot problems include athlete’s foot, warts, and other conditions. Each issue arises from different causes such as fungal or viral infections. More insights on these conditions are available at NIH News in Health.
Maintaining foot health involves practicing good hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and taking preventive measures. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can prevent minor issues from becoming major concerns. This importance is further highlighted in Superfeet’s guide on foot health.
Anatomy of the Foot
The foot is a complex structure made up of bones, muscles, tendons, and arches. Each part has a unique role in providing support, movement, and balance. Understanding the anatomy of the foot helps in maintaining foot health and addressing issues that may arise.
Bones and Their Functions
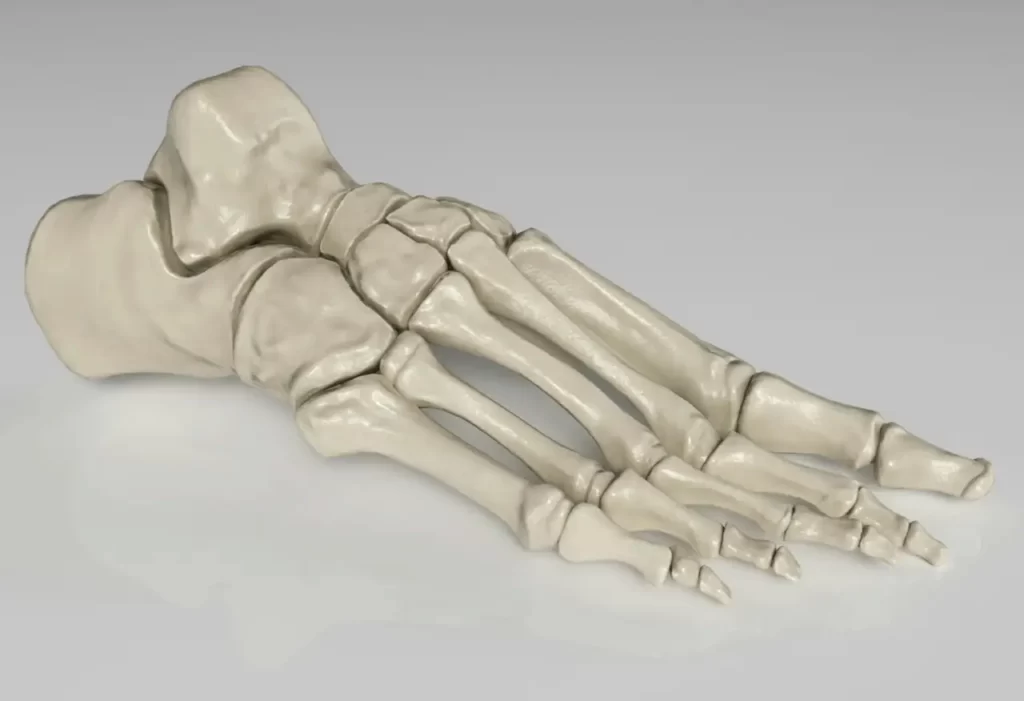
The foot contains 26 bones divided into three sections: the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot. The phalanges are the bones in the toes. Each foot has 14 phalanges, two in the big toe and three in each of the other four toes. The metatarsals are five long bones that form the arch and connect the toes to the midfoot.
The tarsal bones make up the hindfoot and midfoot. The calcaneus, or heel bone, bears most of the body’s weight while standing. The talus connects the foot to the leg bones. Joints between these bones allow for movement and flexibility, essential for walking and running.
Muscles and Tendons
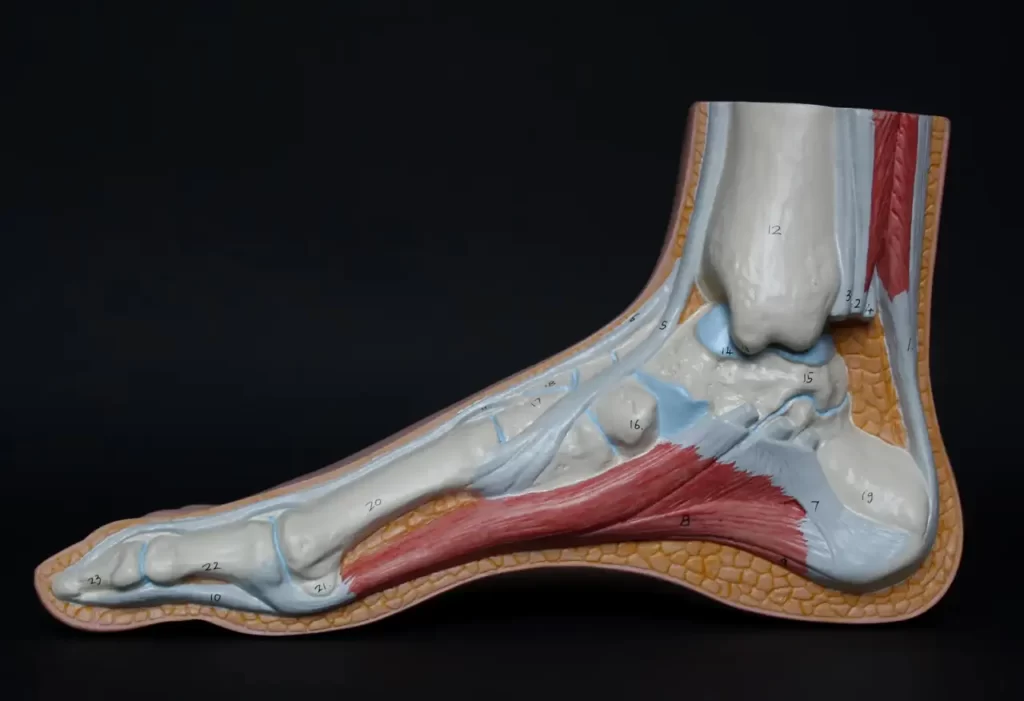
Muscles and tendons in the foot are responsible for moving the toes and allowing the foot to flex and point. Tendons, like the Achilles tendon, connect muscles to bones and help control movements. The plantar fascia is a thick band running along the sole, crucial for arch support and shock absorption.
Muscles can be divided into extrinsic and intrinsic groups. Extrinsic muscles originate in the leg and control larger movements, while intrinsic muscles are found within the foot and assist in fine motor skills and stabilization. These structures work together to maintain balance and adapt to varying surfaces.
Arches and Their Role in Stability
The foot contains three arches: medial, lateral, and transverse. The medial arch is most pronounced, running along the inside of the foot. It helps in absorbing shock and adapting to different surfaces. The lateral arch is on the outer side and provides stability when standing.
The transverse arch runs across the foot and helps distribute weight evenly. Together, these arches form a supportive structure that aids in efficient movement and balance. They also play a key role in preventing injuries by reducing stress on the foot and leg muscles. A well-functioning arch system is essential for maintaining overall foot health.
Common Foot Conditions
Many people encounter foot issues at some point in their lives. Common problems include conditions affecting the heel, toes, and skin of the feet. These can lead to pain, discomfort, and mobility challenges.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a prevalent cause of heel pain, particularly in adults. It involves the inflammation of the thick band of tissue across the bottom of the foot, connecting the heel bone to the toes.
Individuals often experience stabbing pain, especially in the morning. Resting the foot, wearing supportive shoes, and doing stretching exercises can alleviate symptoms. In some cases, physical therapy or medical interventions like corticosteroid injections are necessary. Those with flat feet or high arches are more at risk, so proper footwear is crucial to prevent this condition.
Bunions and Hammertoes
Bunions and hammertoes occur when foot alignment changes, often due to ill-fitting shoes. A bunion is a bony bump at the base of the big toe, causing the toe to turn inward. Hammertoes involve an abnormal bend in the middle joint of a toe, usually the second one.
Both conditions can cause pain and swelling. Choosing shoes with a wide toe box and proper support can help. In severe cases, surgery may be required to correct these deformities. Regular foot exercises can also aid in managing and reducing discomfort, maintaining flexibility, and preventing the conditions from worsening.
Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetic individuals face unique foot challenges, including nerve damage and poor circulation. These issues increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections. Improperly managed, they can lead to serious complications, including amputation.
Regular foot inspections and maintaining good hygiene are essential. Wearing properly fitted shoes and avoiding walking barefoot can protect the feet. Doctors may prescribe special footwear and recommend keeping blood sugar levels under control. Swift treatment of minor foot injuries is vital to prevent escalation into more serious problems.
Athlete’s Foot and Fungal Infections
Athlete’s foot is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It often leads to itching, redness, and peeling. Moist environments, like locker rooms and swimming pools, can foster the growth of the fungus.
Keeping feet dry and clean is key to prevention. Using antifungal creams and powders helps treat infections. Changing socks regularly and choosing breathable footwear can hinder fungal growth. In severe or recurrent cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe stronger antifungal medications for effective management.
Footwear and Foot Health

Proper footwear is essential for foot health, affecting everything from comfort to injury prevention. Different types of shoes and supports play various roles in maintaining the well-being of feet.
Choosing the Right Shoes
Selecting the right shoes involves evaluating factors like size, design, and purpose. Shoes that fit properly can prevent conditions such as bunions and blisters. It’s important to ensure that shoe width and length accommodate natural foot expansion during activities. For insights on how shoe width impacts the comfort and health of your feet, see Harvard Health’s advice on proper fit. Shopping in the afternoon, when feet naturally swell, can help find the best fit. Material is also crucial, with breathable fabrics promoting better foot health by preventing moisture buildup.
The Impact of High Heels
High heels can have significant effects on foot health. They often lead to issues such as foot pain, calluses, and even structural deformities like bunions. Wearing heels changes posture and can stress certain areas of the foot and back. For those who frequently wear heels, it may be helpful to limit their use or choose styles with wider, lower heels to minimize negative effects. Studies found in TIME highlight this risk. Awareness of the potential harm and taking breaks from wearing high heels can help maintain healthier feet.
Orthotics and Insoles
Orthotics and insoles are tools designed to improve foot alignment and provide extra support. They can be especially beneficial for individuals with flat feet, high arches, or specific foot conditions such as plantar fasciitis. These inserts can be custom-made or purchased as pre-fabricated products. The right support redistributes pressure and can prevent pain during physical activities. For more insights, consider reading about footwear’s role in foot health from the Feet First Clinic’s perspective. It’s important to consult with healthcare providers to determine the most suitable type of orthotic for individual needs.
Hygiene and Daily Foot Care
Maintaining foot hygiene is essential for preventing issues such as infections and discomfort. A simple daily routine can make a significant difference.
Daily Cleaning: Wash feet with warm water and mild soap, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal growth. It is important to dry them thoroughly afterward. This step is recommended by foot health specialists like those at Erie Podiatry.
Exfoliation: Regularly removing dead skin helps keep feet soft. Using a gentle foot scrub or pumice stone can help reduce calluses and rough patches.
Moisturization: Apply a moisturizing lotion to keep the skin hydrated. Avoid putting lotion between the toes, as excess moisture can lead to infections.
Nail Care: Trim nails straight across and not too short to avoid ingrown toenails. This practice is advised in several foot care routines like those recommended by Healthline.
Check for Problems: Regularly inspect feet for any signs of blisters, cuts, or other abnormalities. Early detection can prevent more serious issues.
Proper Footwear: Wearing appropriate shoes that fit well helps protect feet from injuries and provides essential support. Foot care experts emphasize the importance of good footwear in maintaining foot health.
These practices are straightforward and effective in maintaining healthy feet. Incorporating them into daily routines ensures comfort and helps prevent common foot problems.
Pediatric Foot Health
Pediatric foot health is crucial for a child’s growth and development. Proper monitoring and addressing common foot issues early can help ensure that children maintain healthy feet as they grow.
Monitoring Child Foot Development
Monitoring a child’s foot development is essential to catch any problems early. From birth, children’s feet are soft and flexible. By the time they reach about six months, feet start forming arches. Observing changes in foot shape and movement is important as they learn to walk.
Regular check-ups with a pediatrician or podiatrist can help track progress. Proper footwear is also critical. Shoes should be supportive and appropriately sized, allowing room for growth. Parents should inspect shoes frequently for wear and fit. Some signs of potential issues include limping, skipping walking milestones, or complaints of pain.
Common Pediatric Foot Issues
Children can experience several foot issues as they grow. Flat feet are quite common and may cause discomfort. In some cases, orthotics or special exercises may help improve alignment. Sever’s disease is another concern, especially among active kids. It involves heel pain due to the growth plate’s inflammation.
Ingrown toenails may also affect children. This often results from improper nail clipping or tight footwear. Bunions and other deformities could develop due to genetic factors. If pain or unusual gait patterns occur, a consultation with a podiatrist who specializes in pediatric care is recommended. Early intervention ensures issues do not worsen and supports an active childhood.
Sports and Athletic Foot Health

Maintaining foot health is essential for athletes, not only to enhance performance but also to prevent injuries. Proper footwear, careful injury prevention strategies, and effective post-activity foot care are crucial components of keeping an athlete’s feet in peak condition.
Injury Prevention
Athletes face a variety of risks concerning their feet. Common injuries include sprains, stress fractures, and tendonitis. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the foot and ankle muscles can help mitigate these issues.
Incorporating exercises that focus on balance and stability is key. Simple activities, like standing on one foot, are effective. It’s also important for athletes to be aware of signs such as persistent pain or swelling, which could indicate a developing injury.
Proper Footwear for Athletes
The right shoes are vital for protecting an athlete’s feet. Shoes should offer support in the arches and cushioning to absorb impact. Sports-specific shoes can enhance performance and reduce injury risk, with features tailored to the demands of each sport.
Regular assessment and replacement of worn shoes are necessary. A good fit is crucial; shoes should provide comfort without squeezing the toes. Socks should also be made of breathable materials to wick away moisture and prevent blisters.
Post-Activity Foot Care
Caring for feet after exercise is as important as prepping them before activity. Athletes should stretch their feet and ankles post-exercise to reduce tension and improve flexibility. Using ice baths or compression socks can help alleviate any soreness or swelling.
Keeping feet clean and dry to avoid fungal infections is essential. Applying moisturizer daily can prevent dry skin. Awareness of any changes in foot appearance or discomfort can catch problems early. It’s wise for athletes to consult a health professional if any persistent issues occur.
Nutrition and Foot Health

Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining healthy feet. Certain nutrients can support bone health and reduce inflammation, which is crucial for foot health. Eating the right foods can prevent issues like fractures and inflammation-related conditions.
Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium helps build strong bones in the feet. Foods like milk, cheese, and leafy greens are excellent calcium sources. Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption, and it’s found in fatty fish and fortified foods. A balance of these nutrients ensures healthy bone development.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties. Found in fish and flaxseeds, these fats may help reduce foot pain and swelling. By incorporating omega-3 rich foods into their diet, individuals can protect their feet from inflammation-related problems.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
A balanced diet helps manage body weight, reducing stress on the feet. Excess body weight can strain feet, leading to conditions like flat feet and stress fractures. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports weight management and, consequently, foot health.
Essential Minerals and Vitamins
Zinc, magnesium, and vitamins C and E can contribute to foot health. They support tissue repair and help in maintaining skin elasticity. Nuts, seeds, and citrus fruits are good sources of these nutrients, assisting in overall foot care.
Including these foods in daily meals can greatly benefit foot health. More insights about nutrition’s impact on foot health are available through resources on the role of nutrition in foot health and maintaining healthy feet through diet.
Aging and Foot Health
As people age, they often face challenges with foot health. Common issues include arthritis affecting joint movement and circulation problems leading to neuropathy. Addressing these concerns can help maintain mobility and reduce discomfort.
Arthritis and Joint Health
Arthritis is a common condition affecting older adults’ feet, especially in the joints. Cartilage wears down over time, causing pain and stiffness. This can lead to difficulty in walking and affect balance. Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent type, often impacting the toes and ankles.
Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can relieve symptoms. Proper footwear with good support may also help. Some individuals find relief with physical therapy or medications that reduce inflammation. Joint-friendly activities like swimming or cycling provide exercise without excessive strain.
Circulation and Neuropathy Issues
Aging often impacts blood circulation in the feet, leading to complications like neuropathy. Conditions such as diabetes can worsen these issues, causing numbness or tingling in the toes and feet. Poor circulation makes healing slower and increases the risk of infections.
Compression socks can improve circulation by providing gentle pressure. Regular foot exams, especially for those with diabetes, are crucial to catch issues early. Maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding smoking are vital steps. Additionally, massage can help stimulate blood flow, offering some relief from discomfort.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy

Rehabilitation is essential for recovering from foot and ankle injuries. It helps restore function, ease pain, and prevent further issues. Physical therapy is a primary method used in rehabilitation and is often the first option for care.
Several exercises can aid recovery by strengthening muscles and improving mobility. Ankle pumps, bent-knee wall stretches, and toe pick-ups are recommended activities. These exercises aim to stretch and strengthen muscles, aiding in restoring stability and flexibility.
A well-structured physical therapy program is important. Each plan is often tailored to specific needs, sometimes involving personalized guidance. If exercises cause increased pain or fail to improve the condition within a week, consulting a therapist is advised. They can offer a thorough assessment and custom treatment plan.
Benefits of Physical Therapy:
- Pain Relief: Helps reduce pain and discomfort.
- Improved Mobility: Increases range of motion and flexibility.
- Muscle Strengthening: Strengthens key muscles in the foot and ankle area.
In some cases, physical therapy partners with orthopedic surgery if necessary. This combined approach ensures comprehensive treatment and recovery, allowing individuals to regain their active lifestyle efficiently.
Individuals can find more information on foot and ankle exercises through resources like Verywell Health or explore specific therapy programs at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Professional Foot Care Services

Professional foot care services play a crucial role in maintaining foot health, addressing issues such as discomfort and deformities, and ensuring overall well-being. They include specialized practices like podiatry and orthopedics, as well as routine check-ups and screenings to catch problems early.
Podiatry and Orthopedics
Podiatry focuses on diagnosing and treating foot, ankle, and lower limb issues. Conditions often treated include bunions, heel pain, and ingrown toenails. Podiatrists provide treatments such as orthotics, which are custom shoe inserts designed to correct foot mechanics. These inserts help relieve pain and improve mobility. Orthopedics, on the other hand, deals with bones, joints, and muscles. Orthopedic specialists address structural problems like fractures and arthritis, using both surgical and non-surgical methods. Together, these fields offer comprehensive care for various foot-related problems. For those interested, more information on specialized foot care is available at Expert Footcare.
Routine Check-ups and Screenings
Routine check-ups are essential for detecting foot health problems before they become serious. Regular visits can help monitor conditions such as diabetes-related foot issues, where early detection is key to preventing complications. Screenings often involve evaluating gait, pressure points, and foot arches to ensure proper function and alignment. These assessments can identify the need for custom footwear or orthotics to prevent pain and injury. In addition, screenings can uncover skin or nail conditions, like fungal infections or corns. Such preventive care helps maintain overall health and comfort, as detailed in the benefits of regular foot care at Advanced Foot Nurse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Foot health involves daily care routines, selecting the right footwear, and using products that support healthy feet. People can also benefit from exercises aimed at improving foot health. Understanding common foot issues and preventive measures is crucial.
How do I maintain a daily foot care routine?
Daily foot care is simple. Wash feet with soap and water, then dry them well, especially between the toes. Applying moisturizer helps keep skin supple, but avoid the areas between the toes to prevent fungal infections.
What are some effective foot health exercises?
Exercises like toe curls and calf stretches can improve flexibility and strength. Practicing balance exercises, such as standing on one foot, supports stability. Walking on soft surfaces like sand also promotes foot health.
Which features should I look for in orthotic supportive shoes?
Look for shoes that provide arch support and a wide toe box. Proper cushioning and a snug heel fit are essential. The shoes should be flexible at the ball of the foot but not too bendy overall.
What are the most common foot health issues and their causes?
Common issues include athlete’s foot, bunions, and corns. These can be caused by fungal infections, ill-fitting shoes, or excessive pressure. Diabetes can lead to more serious issues like diabetic foot ulcers.
How do foot care products contribute to overall foot health?
Products like insoles and medicated creams help support the foot and treat issues like dry skin or fungal infections. Insoles add cushioning and support, while creams can treat specific conditions such as athlete’s foot or cracked skin.
What steps can I take to prevent common foot problems?
Wearing properly fitting shoes and socks made from breathable materials can prevent issues. Regularly inspecting feet for changes reduces risk. Engaging in foot exercises and keeping feet clean and moisturized also helps avoid problems.