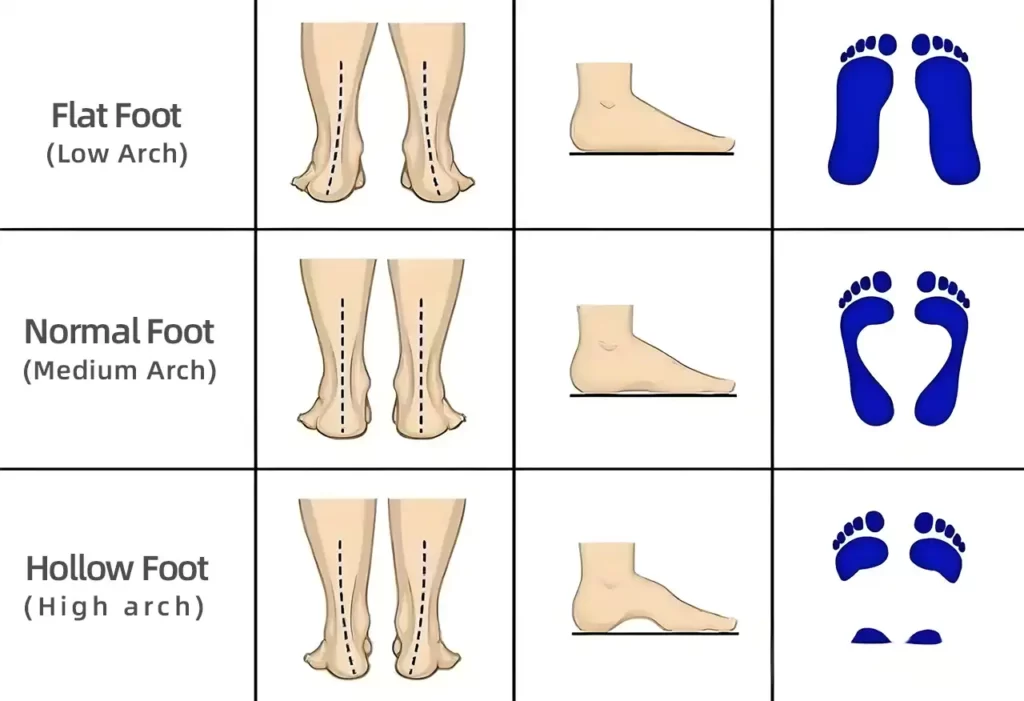
High Arch: Understanding Causes and Treatment Options
High arches, also known as cavus feet, are a common foot condition characterized by an abnormally high arch. People with high arches often face various challenges, such as foot pain and instability, which can impact their daily activities. Understanding the causes and effects of high arches can help those affected seek appropriate treatment and improve their quality of life.
This condition can be hereditary or result from underlying issues, including neurological disorders. Knowing how to identify symptoms will allow individuals to take action sooner. With various management options available, individuals can find the right solutions to alleviate discomfort and maintain foot health.
Exploring high arches reveals crucial insights on prevention and management. Readers can discover how factors like footwear choices and supportive devices can make a difference in their comfort. This article provides valuable information that can empower anyone dealing with this condition to take control of their foot health.
Anatomy of the High Arch
The anatomy of a high arch involves the structure and function of the foot’s arches. Understanding the variations and types helps clarify the characteristics and impacts on various activities.
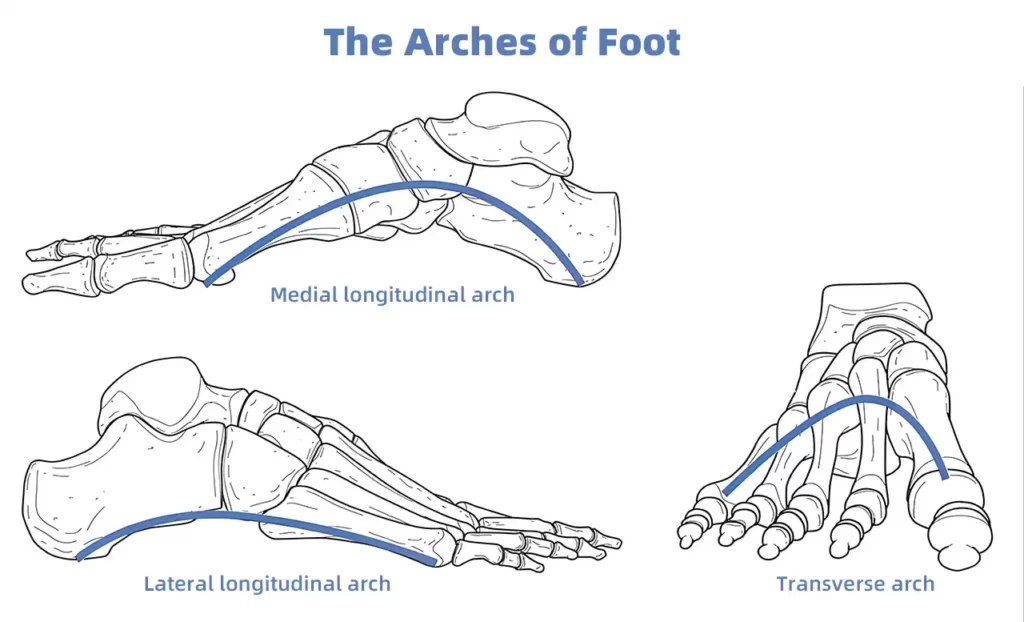
Arch Structure and Function
A high arch, known as pes cavus, is defined by an elevated medial longitudinal arch. This arch is formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones. Key features include:
- Medial Longitudinal Arch: The primary arch running along the inner side of the foot.
- Lateral Longitudinal Arch: Positioned lower than the medial arch.
- Transverse Arch: Spans across the width of the foot.
The function of the high arch is to provide support during walking and running. While it offers excellent stability, it may reduce shock absorption. This can lead to pain in the ball and heel of the foot, as high arches can transfer more stress during movement. Individuals with high arches may experience discomfort due to the lack of flexibility in the foot.
Types of High Arches
High arches can vary based on their specific characteristics and the underlying cause. Two common types are:
- Flexible High Arch: This type allows some movement and can adapt to different surfaces. It generally offers better shock absorption than rigid arches.
- Rigid High Arch: This arch remains fixed and does not flex much. It often results in more discomfort due to limited adaptability during activities.
Both types impact how the foot interacts with the ground. An understanding of these types aids in selecting proper footwear and treatment options, enhancing overall mobility and comfort.
Causes of High Arches
High arches, also known as pes cavus, can arise from various factors. Understanding the underlying causes helps in managing this condition effectively. The main contributors include genetic factors, neurological disorders, and other contributing conditions.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors often play a crucial role in the development of high arches. Many individuals inherit this condition from their parents. It can be part of a hereditary pattern in families. When assessing high arches, healthcare providers often look for family history. If one or both parents have high arches, their children may also be more likely to develop it.
In some cases, high arches may accompany genetic syndromes. These syndromes can include conditions that affect connective tissue and muscle tone. If a child exhibits high arches, it’s important to evaluate their family for similar foot structures. Identifying genetic links can guide recommendations for treatment and management.
Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders are common causes of high arches. Conditions like cerebral palsy, spina bifida, and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease often result in abnormal foot structure. These disorders can affect muscle control and strength in the lower limbs.
In people with these conditions, muscles may become weak or imbalanced. This unevenness can lead to higher arches. Early detection and intervention can be vital. Individuals with neurological conditions should undergo regular assessments. This helps in monitoring foot development and preventing complications.
Other Contributing Conditions
Several other conditions can contribute to high arches. These include trauma, muscle imbalances, and certain types of arthritis. Injuries to the foot can alter its structure, leading to a higher arch.
Muscle imbalances occur when certain muscles in the foot or leg are overdeveloped while others are underdeveloped. This imbalance can push the foot into a higher arch position. Additionally, arthritis can cause changes in joint function, affecting the arch’s support. Identifying these conditions can help in choosing appropriate treatment options.
Identification and Diagnosis
Identifying and diagnosing high arches involves careful evaluation through various methods. This can help healthcare providers develop appropriate treatment plans based on the specific needs of the patient.
Physical Examination
A physical examination is the first step in diagnosing high arches. During this assessment, a healthcare professional looks for visible signs of high arches, such as the shape of the foot and any associated deformities.
The examination often includes a detailed look at the arch height and toe alignment. The clinician may ask the patient to stand and walk to observe foot position and weight distribution.
Additional signs such as calluses on the ball, heel, or side of the foot may also be noted. The patient’s medical history, including any previous foot pain or injuries, is also discussed to gather more context regarding their condition.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging can provide a clearer picture of the foot structure. Common imaging methods include X-rays, which allow for detailed views of the bones and joints.
An X-ray can reveal any abnormal bone positioning or associated issues, such as arthritis. In some cases, MRI or CT scans may be used to examine soft tissue structures, like ligaments and tendons.
These imaging techniques help healthcare providers make accurate diagnoses and rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. They are crucial for understanding the extent of the high arch condition and planning treatment effectively.
Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is a crucial method for diagnosing high arches. It involves closely examining how a person walks and moves. Clinicians observe the foot’s contact with the ground, weight distribution, and the overall walking pattern.
They may use specialized equipment to track motion and pressure points during walking. This data can highlight any irregularities in movement that may be linked to high arches.
Understanding how high arches affect gait is essential for creating a tailored treatment plan. By addressing any issues identified during the analysis, healthcare providers can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
Associated Conditions
High arches can lead to a variety of foot-related issues. These conditions arise due to the unique stress placed on the feet. Pain and discomfort are common consequences.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of the foot. Individuals with high arches often experience extra strain on this tissue. This strain can lead to sharp pain, especially during the first steps in the morning or after long periods of sitting.
Symptoms include:
- Sharp heel pain
- Stiffness in the foot
- Discomfort after prolonged activity
Treatment may involve stretching exercises, orthotic inserts, and physical therapy. In more severe cases, injections or surgery could be considered.
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia refers to pain in the ball of the foot and is frequently associated with high arches. The condition occurs when there is increased pressure on the metatarsal bones, which connect the toes to the foot.

Key factors include:
- High arches causing an uneven weight distribution
- Calluses forming on the affected area
Symptoms often manifest as a burning sensation or a feeling of having a pebble in the shoe. Treatment can involve padded insoles, switching to shoes with better support, and reducing high-impact activities.
Hammer Toe
Hammer toe is a deformity where one or more toes bend downward at the middle joint. This condition can develop due to high arches causing imbalance in foot muscles.
Common consequences include:
- Pain in the affected toe
- Corns or calluses developing on the top of the toe
Treatment often consists of wearing properly fitted shoes that allow for toe movement. In some cases, surgical options may be explored if pain persists. Regular stretching exercises may also help alleviate some discomfort.
Treatment Options
When dealing with high arches, various treatment options are available. These methods can help alleviate pain and improve foot function. Understanding the different approaches can assist individuals in making informed decisions.
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments focus on managing symptoms without surgery. These often include physical therapy, stretching exercises, and pain-relief medications.
Physical therapy can improve strength and flexibility in the feet and legs. A therapist may recommend specific exercises to correct posture and gait issues. Stretching the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia is also common.
Ice therapy can reduce pain and swelling after activities. Using ice packs for 15-20 minutes can provide relief.
Footwear choices are crucial. Supportive shoes with cushioning can offer comfort. It is important to avoid high heels or shoes without arch support.
Orthotics and Bracing
Orthotics are custom-designed shoe inserts that provide extra support. They help redistribute pressure on the foot and can reduce pain. A healthcare provider can recommend specific types based on individual needs.
Over-the-counter orthotics can also be effective. These inserts often come with arch support and cushioning for everyday use.
In some cases, braces might be needed. An ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) can stabilize the foot and provide alignment. Bracing may particularly benefit those experiencing ankle instability or severe pain.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is usually a last resort when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. It aims to correct structural issues in the foot.
One option is a reconstructive surgery to reshape the arch. This can help relieve pain and improve function.
Another type is tendon surgery, which involves lengthening or shortening tendons to support the arch better.
Recovery time can vary based on the specific procedure. Post-surgery rehabilitation typically involves physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
Footwear Considerations
Choosing the right footwear is essential for individuals with high arches. Proper shoes can enhance comfort and support while preventing pain. The following considerations focus on selecting the best shoes and making necessary modifications.
Selecting Appropriate Shoes
When selecting shoes, individuals with high arches should look for specific features. Proper arch support is crucial, as it helps distribute weight evenly. Cushioning in the midsole absorbs shock and reduces pressure on the feet.
Key features to consider:
- Arch Support: Look for shoes that provide firm arch support, especially those designed specifically for high arches.
- Cushioning: Shoes should offer good cushioning in the insole and midsole for comfort.
- Stability: A shoe with a wider base helps maintain balance and support during walking or running.
- Material: Breathable materials enhance comfort and keep feet dry.
Popular choices include brands like Brooks and Saucony, known for their specialized footwear.
Shoe Modifications
Sometimes, customizing shoes enhances comfort for individuals with high arches. Shoe modifications can address specific needs and improve overall fit.
Common modifications include:
- Insoles: Custom orthotic insoles provide tailored support and cushioning. These can be made to fit individual foot shapes and arch heights.
- Heel Lifts: Adding a heel lift can improve alignment and reduce strain. This adjustment can also provide extra support for the plantar fascia.
- Shoe Stretching: Professional stretching can accommodate wider feet or high arches in shoes that may feel tight.
These modifications help create a more comfortable walking experience, reducing the risk of injuries and long-term pain.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Managing high arches can often be addressed through targeted lifestyle changes and home remedies. These methods focus on stretching and strengthening the foot muscles, as well as making adjustments to daily activities to reduce discomfort.
Stretching and Strengthening
Stretching exercises can greatly benefit individuals with high arches. Regularly stretching the calf muscles and Achilles tendon helps improve flexibility. This can reduce strain on the arches.
Some effective stretches include:
- Calf Stretch: Stand facing a wall, place hands on the wall, and keep one foot back while bending the front knee. Hold for 15-30 seconds and switch sides.
- Toe Grab: Sit on a chair and try to pick up small items, like marbles, with toes. Repeat for 5-10 minutes.
Strengthening exercises are also vital. They help support the arches better and can prevent pain.
- Heel Raises: Stand with feet flat and slowly raise heels. Hold for a moment, then lower. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Arch Lifts: While seated, try to lift just the arch of the foot off the ground, keeping the heel and toes down. Hold for a few seconds, then relax.
Activity Modifications
Making small changes in daily routines can alleviate discomfort associated with high arches. Wearing supportive footwear is crucial. Shoes should provide arch support, cushioning, and stability.
When engaging in high-impact activities, consider using orthotic inserts. These can offer additional support and help distribute weight evenly across the foot.
Additionally, individuals should listen to their bodies. If pain occurs during activities, resting and modifying the routine may be necessary. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, are often better choices.
He/she/they should also avoid walking barefoot on hard surfaces to reduce unnecessary pressure on the arches. Simple changes in daily activities can lead to significant comfort improvements.
Implications for Athletes
Athletes with high arches may experience unique challenges and advantages related to their foot structure. Understanding these implications can help optimize performance and reduce the risk of injuries.
Performance and High Arches
Athletes with high arches often benefit in activities requiring speed and agility. Their foot structure allows for better push-off during sprints. This is because less of the foot touches the ground, which can lead to a quicker transition during running.
Studies suggest that a high arch foot type can enhance dynamic balance. This can improve performance in sports that require quick changes in direction. However, it is important to choose shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning to maximize these benefits.
Injury Prevention
While high arches offer performance benefits, they can also increase the risk of specific injuries. Athletes may be prone to issues like ankle sprains and stress fractures. This results from the stiffer foot arch, which can limit flexibility.
To reduce injury risk, it is essential for athletes to engage in specific exercises. These may include calf raises and arch lifts. Stretching and strengthening the muscles around the feet and legs is also beneficial.
Proper footwear is crucial for injury prevention. Shoes that offer sufficient arch support and cushioning can help absorb impact during activities. This will ensure that athletes perform at their best while reducing the chances of injury.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management of high arch feet involves careful monitoring and regular consultations with foot specialists. These practices help in maintaining foot health and addressing any emerging issues.
Monitoring Foot Health
Regularly checking foot health is crucial for individuals with high arches. It is important to inspect the feet for any signs of discomfort or changes. Simple practices include:
- Daily checks: Look for redness, swelling, or calluses.
- Footprints: Examine footprints on a wet surface to assess arch height.
- Pain observation: Take note of any recurring pain in the feet, knees, or back.
Keeping a journal of foot symptoms can help track their frequency and severity. If pain or discomfort increases, it may indicate a need for adjustments in footwear or activity levels. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment options. Regular at-home care can prevent serious complications down the line.
Regular Podiatric Consultations
Consulting a podiatrist regularly is essential for managing high arches effectively. Podiatrists can offer:
- Custom orthotics: Specialized shoe inserts tailored to support high arches.
- Footwear recommendations: Guidance on shoes that provide adequate arch support and stability.
- Therapeutic exercises: A program of exercises that strengthen foot and leg muscles.
It is advisable to schedule visits at least once a year or more frequently if problems arise. Podiatric assessments can help monitor changes in foot structure and function. They can also address any evolving symptoms, ensuring continued comfort and mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
High arches can present unique challenges and advantages. Understanding the best footwear, benefits, and potential issues can help individuals manage their foot health effectively. Additionally, exercises and treatments can further support those with high arches.
What types of shoes are best for someone with a high arch?
Shoes with good arch support and cushioning are ideal for those with high arches. Look for options labeled as supportive or orthotic-friendly. Some recommended brands include Brooks and ASICS, known for their well-cushioned models.
What are the common benefits of having high arches?
Individuals with high arches may experience a unique foot structure that allows for efficient push-off while walking or running. This can lead to enhanced speed in certain activities. They may also find it easier to maintain balance in some sports.
What are typical problems associated with high arches?
High arches are often linked to issues such as foot pain, plantar fasciitis, and ankle instability. They can also lead to increased pressure on the heel and ball of the foot. This pressure may result in conditions like metatarsalgia or stress fractures.
Which exercises are recommended for strengthening high arches?
To strengthen high arches, exercises such as toe curls, calf raises, and arch lifts are beneficial. Stretching the calves and plantar fascia can also improve flexibility and support. These exercises help in developing the muscles that stabilize the arches.
For pain related to high arches, using custom orthotics can provide extra support. Stretching routines may also help alleviate discomfort. In severe cases, consulting with a healthcare professional or physical therapist is advisable.
How can one distinguish if their arch support is excessively high?
Excessively high arch support can lead to discomfort and poor alignment. If one experiences pain after using arch supports, it may be too much. A proper fit should feel comfortable and supportive, not restrictive or painful.






